camera hal之CameraProvider启动流程
3400 Words|Read in about 16 Min|本文总阅读量次
本文主要记录一些关于camera相关的camera hal之CameraProvider启动流程,包含从rc文件启动camera provider服务到最后打开供应商的so来完成初始化。
1Hal module架构
注意这里只进行依赖libhardware库这种方式实现,不讲解legacy方式
HAL module架构主要分为以下3个结构体:
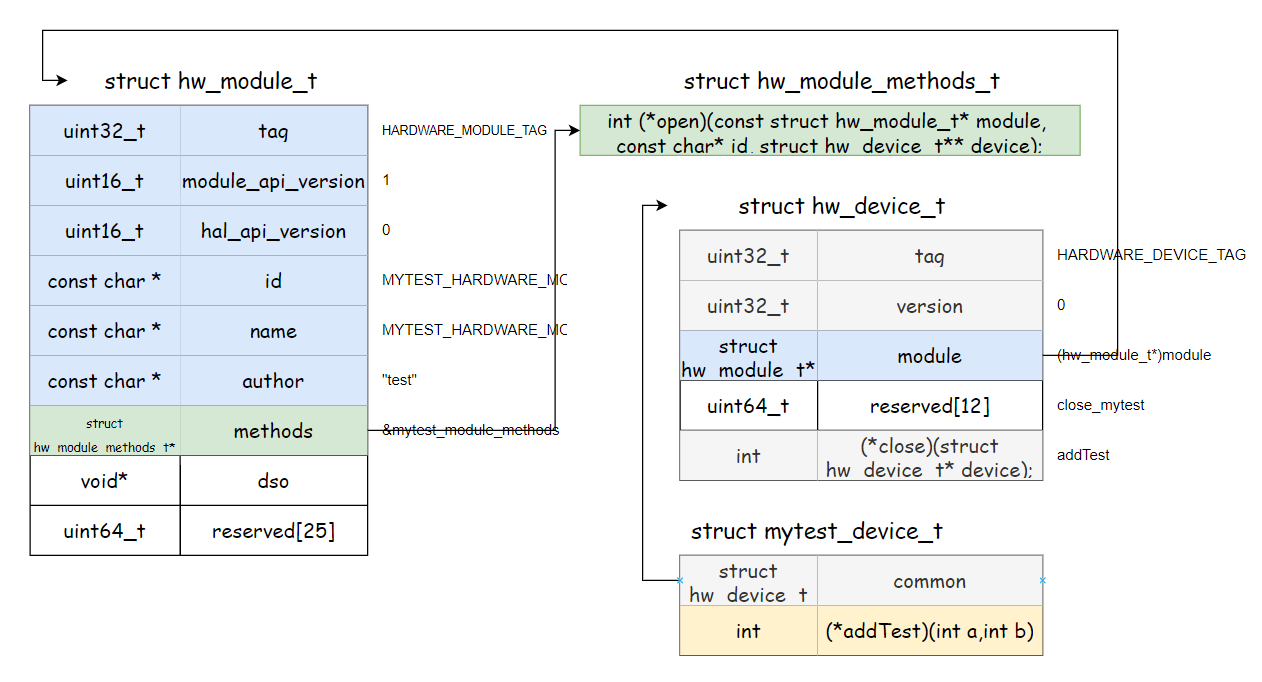
- struct hw_module_t
- struct hw_module_methods_t
- struct hw_device_t
3个结构体是写这个标准方式hal的最关键部分,它们定义是在 hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
1.1struct hw_module_t
1//struct hw_module_t
2// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
3/*
4每个硬件模块都必须有一个名为HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM的数据结构,该数据结构的字段必须以hw_module_t开始,后面是模块相关信息。
5*/
6typedef struct hw_module_t {
7 uint32_t tag;
8 uint16_t module_api_version;
9#define version_major module_api_version
10 uint16_t hal_api_version;
11#define version_minor hal_api_version
12 const char *id;
13 const char *name;
14 const char *author;
15 struct hw_module_methods_t* methods;
16 void* dso;
17
18#ifdef __LP64__
19 uint64_t reserved[32-7];
20#else
21 uint32_t reserved[32-7];
22#endif
23
24} hw_module_t;
1、每一个hardware硬件抽象模块必须定义有一个模块结构体,名字是HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM,即HMI,这个模块结构体第一个成员变量类型必须是hw_module_t
2、hw_module_t的tag的值必须为HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,这个就是来标识是硬件抽象的结构体
3、id这个属性代表这个module的唯一性,即每个硬件抽象模块都会有自己的id
4、methods这个代表每个硬件抽象模块对应的方法结构体,类型hw_module_methods_t
举一个实例化例子
1//实例化HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM: 2 3/* every module must have HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM */ 4struct mytest_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = { 5 .common = { 6 .tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG, 7 .version_major = 1, 8 .version_minor = 0, 9 .id = MYTEST_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, 10 .name = MYTEST_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, 11 .author = "test", 12 .methods = &mytest_module_methods, 13 }, 14};
1.2struct hw_module_methods_t
1// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
2typedef struct hw_module_methods_t {
3 /** Open a specific device */
4 int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
5 struct hw_device_t** device);
6
7} hw_module_methods_t;
在结构体 hw_module_methods_t 中只有一个成员,它是一个函数指针,名字是open,它主要作用就是用来打开硬件抽象层中给的硬件设备。因为一个硬件抽象模块module可以包含多个设备device,所以这里需要指定id。
- moudlue:代表打开硬件设备设备所属模块
- id:代表打开设备的id
- device:这个双重指针,一般是输出内容到这个参数里面,即返回值,用来描述一个打开的硬件设备
1.3struct hw_device_t
1// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
2/**
3每个设备数据结构都必须以hw_device_t开始
4后面是特定于模块的公共方法和属性
5 */
6typedef struct hw_device_t {
7 uint32_t tag;
8 uint32_t version;
9 struct hw_module_t* module;
10#ifdef __LP64__
11 uint64_t reserved[12];
12#else
13 uint32_t reserved[12];
14#endif
15 int (*close)(struct hw_device_t* device);
16} hw_device_t;
其实这个和前面的hw_module_t高度相识,只不过一个代表整个模块一个代表模块的设备 同样总结一下hw_device_t:
1、每个硬件设备都必须自定义一个硬件设备的结构体,第一个成员变量为hw_device_t
2、tag必须为所在的硬件模块HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG,代表他是个硬件设备结构体
3、会有一个close的函数指针,主要是关闭一个硬件设备
4、自定义设备结构体,除了第一个成员hw_device_t外,最重要就是会定义其他成员方法指针,这些方法就是用来对外提供操作硬件设备的
1.4实例
自定义hw_device_t
1struct mytest_device_t {
2 struct hw_device_t common; //第一成员必须为hw_device_t
3 int(*addTest)(int a,int b);
4};
然后进行初始化赋值操作
1struct mytest_device_t * device = NULL;
2device = ( struct mytest_device_t * )malloc(sizeof(*device));
3memset(device, 0, sizeof(*device));
4device->common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
5device->common.version = 0;
6device->common.module = (hw_module_t*)module;
7device->common.close = close_mytest;
8device->addTest = addTest;
上面最重要就是把hw_device_t构造出,而且给成员变量test赋值了具体方法,后面获取了这个hw_device_t就可以调用真正的hal实现方法了
2hardware.c源码流程
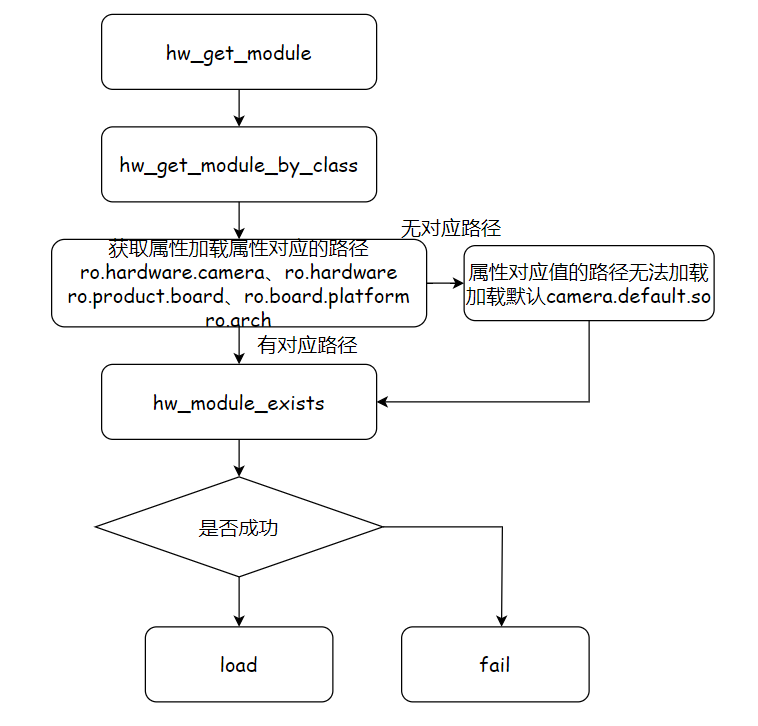
2.1hw_get_module
1//hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
2int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
3{
4 return hw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
5}
6//这里第二个参数为NULL,即inst为NULL
7int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
8 const struct hw_module_t **module)
9{
10 int i = 0;
11 char prop[PATH_MAX] = {0};
12 char path[PATH_MAX] = {0};
13 char name[PATH_MAX] = {0};
14 char prop_name[PATH_MAX] = {0};
15
16
17 if (inst)
18 snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst);
19 else
20 //name就为传入的class_id
21 strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX);
22
23
24 /*
25 这里我们依赖于多次调用dlopen相同的so,将简单地增加一个refcount(而不是加载库的新副本)。
26 我们还假设dlopen()是线程安全的。
27 */
28 //获取属性比如ro.hardware.camera 一般对应会显示厂商mtk,rk,amlogic等
29 snprintf(prop_name, sizeof(prop_name), "ro.hardware.%s", name);
30 if (property_get(prop_name, prop, NULL) > 0) {
31 if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
32 goto found;
33 }
34 }
35 //以此获取下面几个属性值,"ro.hardware"、"ro.product.board"、"ro.board.platform"、"ro.arch"
36 for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT; i++) {
37 if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
38 continue;
39 }
40 if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
41 goto found;
42 }
43 }
44
45 //如果上述属性还是没有对应值,那么加载默认的so,比如default
46 if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, "default") == 0) {
47 goto found;
48 }
49
50 return -ENOENT;
51
52found:
53 //这里开始加载so
54 return load(class_id, path, module);
55}
- hw_module_exists会根据传递进来的name,subname,然后去拼出一个so的文件名字
- load会开始加载对应so,来进行初始化调用
2.2hw_module_exists
检查具有给定名称和子名称的HAL是否存在,如果存在则返回0,否则返回0;否则返回负值。成功之路将包含通往HAL的路径。
1//hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
2#if defined(__LP64__)
3#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1 "/system/lib64/hw"
4#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2 "/vendor/lib64/hw"
5#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH3 "/odm/lib64/hw"
6#else
7#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1 "/system/lib/hw"
8#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2 "/vendor/lib/hw"
9#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH3 "/odm/lib/hw"
10#endif
11
12static int hw_module_exists(char *path, size_t path_len, const char *name,
13 const char *subname)
14{
15 //遍历odm路径的so,比如camera.default.so
16 snprintf(path, path_len, "%s/%s.%s.so",
17 HAL_LIBRARY_PATH3, name, subname);
18 if (path_in_path(path, HAL_LIBRARY_PATH3) && access(path, R_OK) == 0)
19 return 0;
20 //遍历vendor路径的so,比如camera.default.so
21 snprintf(path, path_len, "%s/%s.%s.so",
22 HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name, subname);
23 if (path_in_path(path, HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2) && access(path, R_OK) == 0)
24 return 0;
25
26#ifndef __ANDROID_VNDK__
27 snprintf(path, path_len, "%s/%s.%s.so",
28 HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name, subname);
29 if (path_in_path(path, HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1) && access(path, R_OK) == 0)
30 return 0;
31#endif
32
33 return -ENOENT;
34}
如果不存在,直接返回错误,标识无法加载对应的hal的so;如果存在,那么加载对应的so,比如/vendor/lib/hw/camera.default.so
2.3load
1//hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
2/ * *
3*如果成功,加载变量定义的文件
4*返回dlopen 句柄和hmi。
5* @return 0 =成功,!0 =失败。
6* /
7static int load(const char *id,
8 const char *path,
9 const struct hw_module_t **pHmi)
10{
11 int status = -EINVAL;
12 void *handle = NULL;
13 struct hw_module_t *hmi = NULL;
14#ifdef __ANDROID_VNDK__
15 const bool try_system = false;
16#else
17 const bool try_system = true;
18#endif
19 //加载so,方法是android封装了dlopen
20 //特别注意:加载so的时候,如果so中有全局变量会优先构造或者初始化
21 handle = android_load_sphal_library(path, RTLD_NOW);
22 if (handle == NULL) {
23 char const *err_str = dlerror();
24 ALOGE("load: module=%s\n%s", path, err_str?err_str:"unknown");
25 status = -EINVAL;
26 goto done;
27 }
28
29 //加载完so,寻找struct hal_module_info,并且持有hmi句柄
30 const char *sym = HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR;
31 hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);
32 if (hmi == NULL) {
33 ALOGE("load: couldn't find symbol %s", sym);
34 status = -EINVAL;
35 goto done;
36 }
37
38 //传入的id和so定义的id是否一致,不一致说明加载错误
39 if (strcmp(id, hmi->id) != 0) {
40 ALOGE("load: id=%s != hmi->id=%s", id, hmi->id);
41 status = -EINVAL;
42 goto done;
43 }
44
45 hmi->dso = handle;
46
47 /* success */
48 status = 0;
49
50 done:
51 if (status != 0) {
52 hmi = NULL;
53 if (handle != NULL) {
54 dlclose(handle);
55 handle = NULL;
56 }
57 } else {
58 //走到这里,hmi句柄不会释放,一直持有
59 ALOGV("loaded HAL id=%s path=%s hmi=%p handle=%p",
60 id, path, hmi, handle);
61 }
62
63 *pHmi = hmi;
64
65 return status;
66}
特别注意:加载so的时候,如果so中有全局变量会优先构造或者初始化
dlopen()是一个强大的库函数。该函数将打开一个新库,并把它装入内存。该函数主要用来加载库中的符号,这些符号在编译的时候是不知道的。dlsym是一个计算机函数,功能是根据动态链接库操作句柄与符号,返回符号对应的地址,不但可以获取函数地址,也可以获取变量地址。
2.4实例说明
以笔者努比亚Z50SP手机为例
1-????????? ? ? ? ? ? audio.bluetooth_qti.default.so
2-????????? ? ? ? ? ? audio.primary.default.so
3-????????? ? ? ? ? ? audio.primary.kalama.so
4-????????? ? ? ? ? ? audio.r_submix.default.so
5-????????? ? ? ? ? ? audio.usb.default.so
6-????????? ? ? ? ? ? camera.qcom.so
7-????????? ? ? ? ? ? com.dsi.ant@1.0-impl.so
8-????????? ? ? ? ? ? com.qti.chi.offline.so
9-????????? ? ? ? ? ? com.qti.chi.override.so
10-????????? ? ? ? ? ? consumerir.zte.so
11-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11056 2009-01-01 08:00 gralloc.default.so
12-????????? ? ? ? ? ? local_time.default.so
13-????????? ? ? ? ? ? power.default.so
可以看出camera使用的是高通的so,audio使用的是kalama,另外的usbaudio,gralloc和power使用的是默认的so
对应属性查看,跟上面的so加载对应上了
1PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.board.platform
2[ro.board.platform]: [kalama]
3PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.arch
41|PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.hardware.camera
51|PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.hardware
6[ro.hardware]: [qcom]
7[ro.hardware.consumerir]: [zte]
8[ro.hardware.egl]: [adreno]
9[ro.hardware.keystore_desede]: [true]
10[ro.hardware.vulkan]: [adreno]
11PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.product.board
12[ro.product.board]: [kalama]
13PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.board.platform
14[ro.board.platform]: [kalama]
15PQ82A02:/ $ getprop |grep ro.arch
161|PQ82A02:/ $
3HAL module流程
上面只是一个个的定义好硬件抽象模块的步骤,接下来是要要怎么使用上面的hardware接口进行调用到相关的hal方法呢?
- 通过hw_get_module(char* id, struct hw_module_t ** module) 方法**获取一个硬件抽象模块的指针**
- 通过模块调用module->common.methods->open()方法获取一个硬件抽象即hw_device_t的指针
- 使用硬件抽象设备的hw_device_t指针调用具体的hal实现方法,比如上面 mytest_dev->addTest
相关调用hal的代码如下:
1mytest_module_t* module;
2//1.获取hw_module_t
3if (0 == hw_get_module(MYTEST_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, (const hw_module_t**)&module) ) {
4 //2.调用methods的open方法,目的获取hw_device_t的指针
5 if (0 == ((hw_module_t*)module)->methods->open((hw_module_t*)module,
6 MYTEST_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
7 (struct hw_device_t**)&mytest_device)) {
8 //3.利用获取的mytest_device,调用对于的方法
9 int result = mytest_device->addTest(1,2);
10 }
11}
4CameraProvider
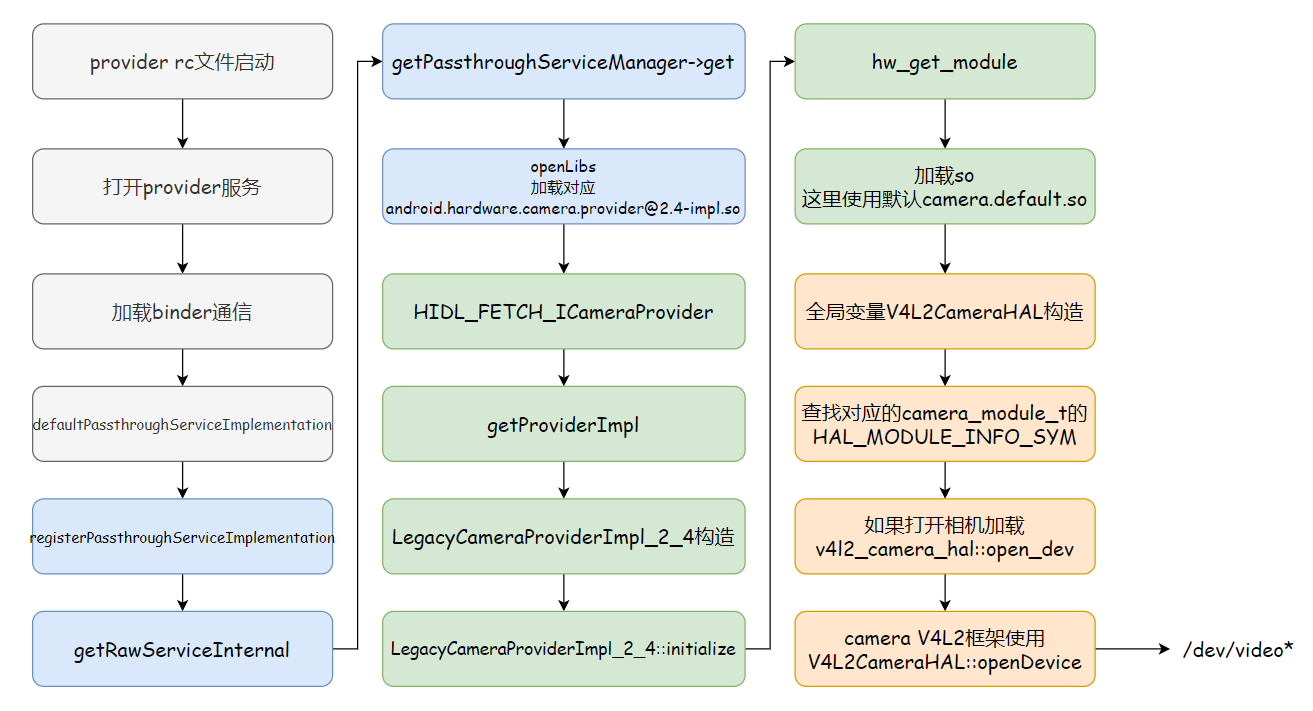
Camera HAL运行在CameraProvider进程当中,目前已经到2.7版本,但是使用最多的是2.4版本,2.4是加入Treble机制后CameraProvider进程的第一个版本,所以我们先从这里开始。
4.1rc启动cameraprovider service
CameraProvider进程是一个native服务,通过init.rc启动
1# hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64.rc
2#真正的进程名称是android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64
3service vendor.camera-provider-2-4 /vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64
4 interface android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider legacy/0
5 class hal
6 user cameraserver
7 group audio camera input drmrpc
8 ioprio rt 4
9 capabilities SYS_NICE
10 task_profiles CameraServiceCapacity MaxPerformance
由上可以看出,进程启动时执行的时二进制/vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64
4.2查找进程的入口
下面我们从Android.bp中找到该二进制的入口文件和入口函数。
1// hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/Android.bp
2...
3cc_binary {
4 name: "android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64",
5 defaults: ["camera_service_defaults"],
6 compile_multilib: "64",
7 init_rc: ["android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64.rc"],
8}
9cc_defaults {
10 name: "camera_service_defaults",
11 defaults: ["hidl_defaults"],
12 proprietary: true,
13 relative_install_path: "hw",
14 srcs: ["service.cpp"], // 二进制入口肯定时service.cpp里面的main函数
15 shared_libs: [
16 "android.hardware.camera.common@1.0",
17 "android.hardware.camera.device@1.0",
18 "android.hardware.camera.device@3.2",
19 "android.hardware.camera.device@3.3",
20 "android.hardware.camera.device@3.4",
21 "android.hardware.camera.device@3.5",
22 "android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4",
23 "android.hardware.graphics.mapper@2.0",
24 "android.hardware.graphics.mapper@3.0",
25 "android.hardware.graphics.mapper@4.0",
26 "android.hidl.allocator@1.0",
27 "android.hidl.memory@1.0",
28 "libbinder",
29 "libcamera_metadata",
30 "libcutils",
31 "libhardware",
32 "libhidlbase",
33 "liblog",
34 "libutils",
35 ],
36 static_libs: [
37 "android.hardware.camera.common@1.0-helper",
38 ],
39 header_libs: [
40 "camera.device@3.4-external-impl_headers",
41 "camera.device@3.4-impl_headers",
42 "camera.device@3.5-external-impl_headers",
43 "camera.device@3.5-impl_headers",
44 ],
45}
46...
从以上Android.bp文件中可以看出,/vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64只包含了一个源文件service.cpp,那么入口函数肯定就是这个cpp里面的main函数了。
1// hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/service.cpp
2int main()
3{
4 ALOGI("CameraProvider@2.4 legacy service is starting.");
5 // /dev/vndbinder
6 // 这里表示Camera hal可以跟其他 vendor hal进程通过binder通信,否则不可以
7 android::ProcessState::initWithDriver("/dev/vndbinder");
8
9 // b/166675194
10 if (property_get_bool("ro.vendor.camera.provider24.disable_mem_init", false)) {
11 if (mallopt(M_BIONIC_ZERO_INIT, 0) == 0) {
12 ALOGE("Disabling heap initialization failed.");
13 }
14 }
15
16 status_t status;
17 if (kLazyService) {
18 status = defaultLazyPassthroughServiceImplementation<ICameraProvider>("legacy/0",
19 /*maxThreads*/ 6);
20 } else {
21 // 启动时会执行下面的函数,这里记下这里的泛型类型为ICameraProvider,还有两个参数,后面有用
22 status = defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation<ICameraProvider>("legacy/0",
23 /*maxThreads*/ 6);
24 }
25 return status;
26}
4.3服务调用
defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation的实现如下
1// system/libhidl/transport/include/hidl/LegacySupport.h
2// 这里的两个泛型参数都为ICameraProvider
3template <class Interface, class ExpectInterface = Interface>
4__attribute__((warn_unused_result)) status_t defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation(
5 const std::string& name, size_t maxThreads = 1) {
6 // 设置该进程中binder通信线程池的最大线程数,这里maxThreads=6
7 configureRpcThreadpool(maxThreads, true);
8 // 注意这里的泛型类型为ICameraProvider, 参数name为legacy/0
9 status_t result = registerPassthroughServiceImplementation<Interface, ExpectInterface>(name);
10
11 if (result != OK) {
12 return result;
13 }
14 // 把当前线程也就是主线程加入binder线程池
15 joinRpcThreadpool();
16 return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
17}
- 设置该进程中binder通信线程池的最大线程数,这里maxThreads=6
- 注册服务,使用泛型,name为legacy/0
- 把当前线程也就是主线程加入binder线程池
4.4注册服务
1// system/libhidl/transport/include/hidl/LegacySupport.h
2template <class Interface, class ExpectInterface = Interface>
3__attribute__((warn_unused_result)) status_t registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(
4 const std::string& name = "default") {
5 // 这里Interface和ExpectInterface是ICameraProvider
6 // ICameraProvider::descriptor为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
7 // 至于ICameraProvider::descriptor的值哪里赋值的,后面细讲
8 return registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(Interface::descriptor,
9 ExpectInterface::descriptor, name);
10}
11
12// system/libhidl/transport/LegacySupport.cpp
13__attribute__((warn_unused_result)) status_t registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(
14 const std::string& interfaceName, const std::string& expectInterfaceName,
15 const std::string& serviceName) {
16 // 这里前两个参数为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider,
17 // 第三个参数为lambda表达式的一个函数,该函数传入两个参数,然后执行registerAsServiceInternal
18 // 第四个参数为legacy/0
19 return details::registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(
20 interfaceName, expectInterfaceName,
21 [](const sp<IBase>& service, const std::string& name) {
22 return details::registerAsServiceInternal(service, name);
23 },
24 serviceName);
25}
26
27
28__attribute__((warn_unused_result)) status_t registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(
29 const std::string& interfaceName, const std::string& expectInterfaceName,
30 RegisterServiceCb registerServiceCb, const std::string& serviceName) {
31 // 这是一个关键函数,第一个参数为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
32 // 第二个参数为 legacy/0
33 // 我们下面先分析这个函数,然后再继续
34 sp<IBase> service =
35 getRawServiceInternal(interfaceName, serviceName, true /*retry*/, true /*getStub*/);
36
37 // 这里我们把后面的代码先省略掉,等getRawServiceInternal函数讲完之后再继续往下分析
38 ...
39}
- 打开camera hal的so库,初始化Camera Hal,比如获取camera numbers,在getRawServiceInternal里实现
- 将camera hal注册为binder服务,在registerServiceCb里实现,也就是上一步的lamda函数,最终调用的是 registerAsServiceInternal
4.5获取原生内部服务
1// system/libhidl/transport/ServiceManagement.cpp
2// 第一个参数为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
3// 第二个参数为 legacy/0
4// 后两个参数都为true
5sp<::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase> getRawServiceInternal(const std::string& descriptor,
6 const std::string& instance,
7 bool retry, bool getStub) {
8 using Transport = IServiceManager1_0::Transport;
9 sp<Waiter> waiter;
10
11 sp<IServiceManager1_1> sm;
12 Transport transport = Transport::EMPTY;
13 if (kIsRecovery) {
14 transport = Transport::PASSTHROUGH;
15 } else {
16 sm = defaultServiceManager1_1();
17 if (sm == nullptr) {
18 ALOGE("getService: defaultServiceManager() is null");
19 return nullptr;
20 }
21
22 // transport类型决定了当前HAL是绑定式还是直通式
23 Return<Transport> transportRet = sm->getTransport(descriptor, instance);
24
25 if (!transportRet.isOk()) {
26 ALOGE("getService: defaultServiceManager()->getTransport returns %s",
27 transportRet.description().c_str());
28 return nullptr;
29 }
30 transport = transportRet;
31 }
32
33 const bool vintfHwbinder = (transport == Transport::HWBINDER); // true
34 const bool vintfPassthru = (transport == Transport::PASSTHROUGH); // false
35 const bool trebleTestingOverride = isTrebleTestingOverride(); // false
36 const bool allowLegacy = !kEnforceVintfManifest || (trebleTestingOverride && isDebuggable()); // false
37 const bool vintfLegacy = (transport == Transport::EMPTY) && allowLegacy; // false
38
39 // 因为参数getStub为true,所以这里的for循环不进入,不执行
40 ...
41
42 // getStub为true,进入这里的if语句
43 if (getStub || vintfPassthru || vintfLegacy) {
44 // getPassthroughServiceManager 返回new PassthroughServiceManager()
45 const sp<IServiceManager1_0> pm = getPassthroughServiceManager();
46 if (pm != nullptr) {
47 // 下面单独分析PassthroughServiceManager的get函数
48 sp<IBase> base = pm->get(descriptor, instance).withDefault(nullptr);
49 // getStub为true, trebleTestingOverride为false,这里的if进不去
50 if (!getStub || trebleTestingOverride) {
51 base = wrapPassthrough(base);
52 }
53 return base;
54 }
55 }
56
57 return nullptr;
58}
-
getTransport,会读取/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xml文件来获取当前transport类型, transport类型决定了当前HAL是绑定式还是直通式
// 这里最终会去读取/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xml文件来获取当前transport类型 // 初始文件在device/xxx/manifest.xml,编译时跟其他manifest // 一起写入/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xml,定义如下:
1<!--/vendor/etc/vintf/manifest.xml --> 2 <manifest version="1.0" type="device" target-level="3"> 3 <hal format="hidl"> 4 <name>android.hardware.camera.provider</name> 5 <transport>hwbinder</transport> 6 <fqname>@2.4::ICameraProvider/legacy/0</fqname> 7 </hal> 8 </manifest> -
getPassthroughServiceManager,获取对应服务的代理对象
-
PassthroughServiceManager.get,会打开对应的lib,即android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so
4.6打开对应的lib
1// system/libhidl/transport/ServiceManagement.cpp
2// descriptor: android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
3// instance: legacy/0
4sp<IBase> base = pm->get(descriptor, instance)
5Return<sp<IBase>> get(const hidl_string& fqName,
6 const hidl_string& name) override {
7 sp<IBase> ret = nullptr;
8
9 // 主要就是执行了openLibs函数,我们先把参数理一下,然后在进入openLibs函数进行分析
10 // 第一个参数fqName: android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
11 // 第二个参数是一个lamda函数,这个函数有三个参数,这里主要是这个lamda函数的实现,
12 openLibs(fqName, [&](void* handle, const std::string &lib, const std::string &sym) {
13 ...
14 }
15}
16
17// openLibs函数实现
18static void openLibs(
19 // fqName: android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
20 const std::string& fqName,
21 // eachLib: 就是上面提到的lamda函数
22 const std::function<bool /* continue */ (void* /* handle */, const std::string& /* lib */,
23 const std::string& /* sym */)>& eachLib) {
24 //fqName looks like android.hardware.foo@1.0::IFoo
25 // 用::符号将参数分割为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4和ICameraProvider
26 size_t idx = fqName.find("::");
27
28 if (idx == std::string::npos ||
29 idx + strlen("::") + 1 >= fqName.size()) {
30 LOG(ERROR) << "Invalid interface name passthrough lookup: " << fqName;
31 return;
32 }
33
34 // 这里拿到的就是android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4
35 std::string packageAndVersion = fqName.substr(0, idx);
36 // 这里拿到的就是 ICameraProvider
37 std::string ifaceName = fqName.substr(idx + strlen("::"));
38
39 // prefix为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl
40 const std::string prefix = packageAndVersion + "-impl";
41 // sym为 HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider
42 const std::string sym = "HIDL_FETCH_" + ifaceName;
43
44 // 到此,上面参数已经解析完毕,下面根据prefix和sym来执行
45
46 constexpr int dlMode = RTLD_LAZY;
47 void* handle = nullptr;
48
49 dlerror(); // clear
50
51 static std::string halLibPathVndkSp = details::getVndkSpHwPath();
52 //这里的变量分别为"/odm/lib64/hw/", "/vendor/lib64/hw/", "/apex/com.android.vndk.v33/lib64/hw/"
53 std::vector<std::string> paths = {
54 HAL_LIBRARY_PATH_ODM, HAL_LIBRARY_PATH_VENDOR, halLibPathVndkSp,
55#ifndef __ANDROID_VNDK__
56 //这里的变量为"/system/lib64/hw/"
57 HAL_LIBRARY_PATH_SYSTEM,
58#endif
59 };
60
61 // 条件为false,不进入
62 if (details::isTrebleTestingOverride()) {
63 // Load HAL implementations that are statically linked
64 handle = dlopen(nullptr, dlMode);
65 if (handle == nullptr) {
66 const char* error = dlerror();
67 LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to dlopen self: "
68 << (error == nullptr ? "unknown error" : error);
69 } else if (!eachLib(handle, "SELF", sym)) {
70 return;
71 }
72 }
73 // 在paths的几个路径中寻找android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so文件
74 // 我们到设备里查看一下,发现在/vendor/lib64/hw目录下,因为是64位系统,所以/vendor/lib/hw/是不会遍历的
75 for (const std::string& path : paths) {
76 std::vector<std::string> libs = findFiles(path, prefix, ".so");
77
78 for (const std::string &lib : libs) {
79 // fullPath=/vendor/lib64/hw/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so
80 const std::string fullPath = path + lib;
81
82 if (kIsRecovery || path == HAL_LIBRARY_PATH_SYSTEM) {
83 handle = dlopen(fullPath.c_str(), dlMode);
84 } else {
85#if !defined(__ANDROID_RECOVERY__) && defined(__ANDROID__)
86 // 最终执行这里,load so库,拿到handle
87 handle = android_load_sphal_library(fullPath.c_str(), dlMode);
88#endif
89 }
90
91 if (handle == nullptr) {
92 const char* error = dlerror();
93 LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to dlopen " << lib << ": "
94 << (error == nullptr ? "unknown error" : error);
95 continue;
96 }
97 // 还记得eachLib函数吗,就是上面省略掉的lamda回调函数,下面开始分析
98 if (!eachLib(handle, lib, sym)) {
99 return;
100 }
101 }
102 }
103}
- 分割传入的字符串fqName,packageAndVersion为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4,ifaceName为ICameraProvider
- 拼接字符串prefix为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl,sym为HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider
- 查找几个目录下对应的so文件,分别为"/odm/lib64/hw/", “/vendor/lib64/hw/”, “/apex/com.android.vndk.v33/lib64/hw/”
- 打开对应的so文件,拿到对应的句柄,获取sym的变量,即为HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider
4.7openLib回调匿名内部函数
1// system/libhidl/transport/ServiceManagement.cpp
2// fqName: android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4::ICameraProvider
3// name: legacy/0
4Return<sp<IBase>> get(const hidl_string& fqName,
5 const hidl_string& name) override {
6 sp<IBase> ret = nullptr;
7 // 这里的handle为dlopen /vendor/lib64/hw/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so后的handle
8 // lib参数为android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so
9 // sym参数为HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider
10 openLibs(fqName, [&](void* handle, const std::string &lib, const std::string &sym) {
11 IBase* (*generator)(const char* name);
12 // 通过dlsym在android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so中找到HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider的地址
13 *(void **)(&generator) = dlsym(handle, sym.c_str());
14 if(!generator) {
15 const char* error = dlerror();
16 LOG(ERROR) << "Passthrough lookup opened " << lib << " but could not find symbol "
17 << sym << ": " << (error == nullptr ? "unknown error" : error)
18 << ". Keeping library open.";
19
20 // dlclose too problematic in multi-threaded environment
21 // dlclose(handle);
22
23 return true; // continue
24 }
25 // 执行HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider函数,参数为legacy/0
26 ret = (*generator)(name.c_str());
27
28 using ::android::hardware::details::getDescriptor;
29 std::string actualFqName = getDescriptor(ret.get());
30 CHECK(actualFqName.size() > 0);
31 registerReference(actualFqName, name);
32 return false;
33 });
34
35 return ret;
36}
执行HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider函数,参数为legacy/0,并将其注册到sm服务中
4.8HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider函数
so调用用于获取对应ICameraProvider入口,调用CameraProvider构造函数
1// hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/CameraProvider_2_4.cpp
2// 参数name为legacy/0
3ICameraProvider* HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider(const char* name) {
4 using namespace android::hardware::camera::provider::V2_4::implementation;
5 ICameraProvider* provider = nullptr;
6 if (strcmp(name, kLegacyProviderName) == 0) {
7 // 执行这里
8 provider = getProviderImpl<LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4>();
9 } else if (strcmp(name, kExternalProviderName) == 0) {
10 provider = getProviderImpl<ExternalCameraProviderImpl_2_4>();
11 } else {
12 ALOGE("%s: unknown instance name: %s", __FUNCTION__, name);
13 }
14
15 return provider;
16}
17
18// 创建CameraProvider对象并返回,在CameraProvider的构造函数中,会执行IMPL的构造函数,
19// 也就是LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4的构造函数
20template<typename IMPL>
21CameraProvider<IMPL>* getProviderImpl() {
22 CameraProvider<IMPL> *provider = new CameraProvider<IMPL>();
23 if (provider == nullptr) {
24 ALOGE("%s: cannot allocate camera provider!", __FUNCTION__);
25 return nullptr;
26 }
27 if (provider->isInitFailed()) {
28 ALOGE("%s: camera provider init failed!", __FUNCTION__);
29 delete provider;
30 return nullptr;
31 }
32 return provider;
33}
LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4的构造函数实现
1// hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/CameraProvider_2_4.h
2template<typename IMPL>
3struct CameraProvider : public ICameraProvider {
4 CameraProvider() : impl() {}
5};
6// hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4.cpp
7LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4::LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4() :
8 camera_module_callbacks_t({sCameraDeviceStatusChange,
9 sTorchModeStatusChange}) {
10 mInitFailed = initialize();
11}
这里开始camera provider真是实现的初始化操作
上面创建了LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4对象,并执行了其初始化函数initialize()。
总结一句其实就是CameraProvider进程启动时加载android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-impl.so库并执行LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4的初始化函数。
4.9LegacyCameraProviderImpl初始化
1// hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4.cpp
2// initialize()函数的实现
3bool LegacyCameraProviderImpl_2_4::initialize() {
4 camera_module_t *rawModule;
5 // 通过hw_get_module加载对应的so库,这个库是由厂商提供的,一般只以so库的方式提供,
6 // 不过也有情况会提供so库的源码,不过核心的地方还是会封装在别的so库中。
7 int err = hw_get_module(CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
8 (const hw_module_t **)&rawModule);
9 if (err < 0) {
10 ALOGE("Could not load camera HAL module: %d (%s)", err, strerror(-err));
11 return true;
12 }
13 ...
14}
上面的hw_get_module是不是比较眼熟,就是上面2小结里面的流程
关于camera里面的load补充一下
1// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera_common.h
2// 别忘了参数值:
3 // id: camera
4 // path: 上面找到的路径,假设为 /vendor/lib64/hw/
5static int load(const char *id,
6 const char *path,
7 const struct hw_module_t **pHmi)
8{
9 ...
10 handle = android_load_sphal_library(path, RTLD_NOW);
11
12 //这里是重中之重
13 const char *sym = HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR;
14 hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);
15 if (hmi == NULL) {
16 ALOGE("load: couldn't find symbol %s", sym);
17 status = -EINVAL;
18 goto done;
19 }
20
21 /* Check that the id matches */
22 if (strcmp(id, hmi->id) != 0) {
23 ALOGE("load: id=%s != hmi->id=%s", id, hmi->id);
24 status = -EINVAL;
25 goto done;
26 }
27
28 hmi->dso = handle;
29
30 /* success */
31 status = 0;
32
33 done:
34 if (status != 0) {
35 hmi = NULL;
36 if (handle != NULL) {
37 dlclose(handle);
38 handle = NULL;
39 }
40 } else {
41 ALOGV("loaded HAL id=%s path=%s hmi=%p handle=%p",
42 id, path, hmi, handle);
43 }
44
45 // 返回hmi,这个是名称为“HMI”的结构体变量在so库中的地址,类型为hw_module_t
46 // 但是结构体定义的地方却是camera_module_t类型的,那么这两者有啥关系呢
47 // 通过查看定义就知道camera_module_t结构体的第一个成员就是hw_module_t common
48 // 这样是为了方便直接调用.common.methods.open函数吧
49 *pHmi = hmi;
50
51 return status;
52}
关于打开对应so之后
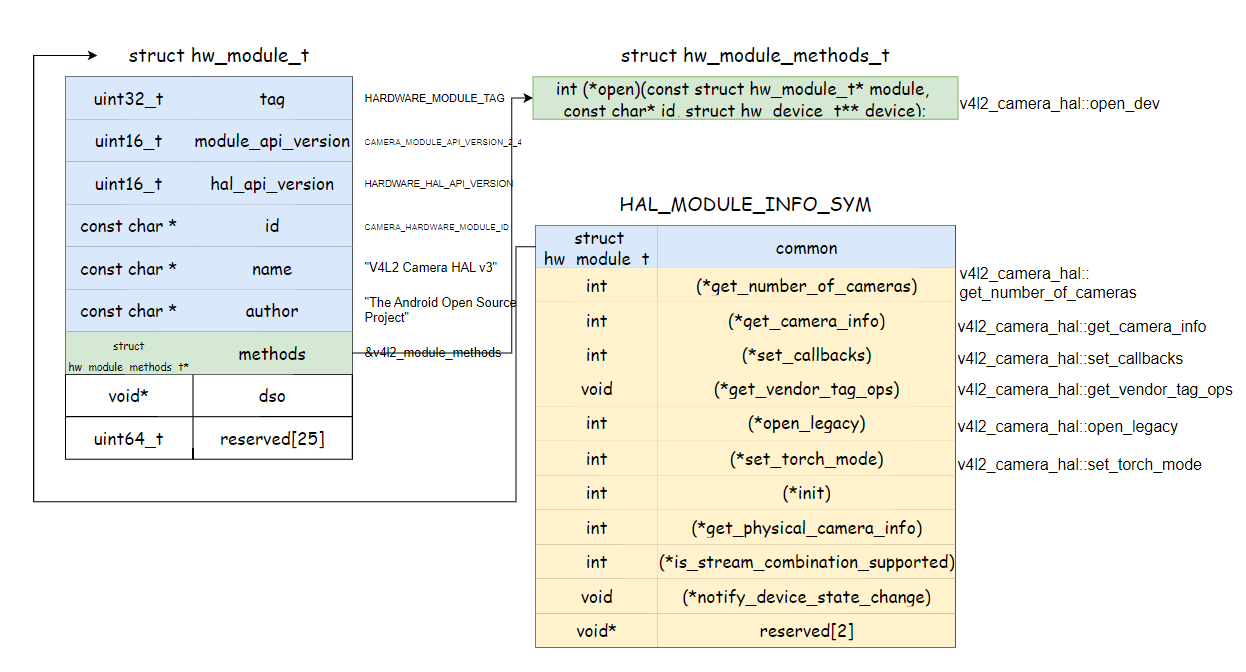
1// 上面的无非就是load so,拿到handle,接下来就是关键之处了 2/* Get the address of the struct hal_module_info. */ 3// HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR的定义如下 4// #define HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR "HMI" 5// 所以sym也为 "HMI” 6// 注意这个值是固定的,是实现hw_get_module实现的一个标准 7// 厂商定义hal的时候,在so库里面必须定义一个结构体名称为“HMI” 8// 这里是调用so库的入口 9// 我们以Google的默认 camera hal so为例看下 10// 这里定义了一个类型为camera_module_t,名称为HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM的结构体 11// 而HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM的名称就是 “HMI” 12// 找到这里后会调用该结构体变量的.common.methods.open函数 13// 对应到这里的话就是v4l2_module_methods.open 14// 最终会调用v4l2_camera_hal::open_dev,如下 15// static hw_module_methods_t v4l2_module_methods = { 16// .open = v4l2_camera_hal::open_dev}; 17// camera_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM __attribute__((visibility("default"))) = { 18// .common = 19// { 20// .tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG, 21// .module_api_version = CAMERA_MODULE_API_VERSION_2_4, 22// .hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION, 23// .id = CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, 24// .name = "V4L2 Camera HAL v3", 25// .author = "The Android Open Source Project", 26// .methods = &v4l2_module_methods, 27// .dso = nullptr, 28// .reserved = {0}, 29// }, 30// .get_number_of_cameras = v4l2_camera_hal::get_number_of_cameras, 31// .get_camera_info = v4l2_camera_hal::get_camera_info, 32// .set_callbacks = v4l2_camera_hal::set_callbacks, 33// .get_vendor_tag_ops = v4l2_camera_hal::get_vendor_tag_ops, 34// .open_legacy = v4l2_camera_hal::open_legacy, 35// .set_torch_mode = v4l2_camera_hal::set_torch_mode, 36// .init = nullptr, 37// .get_physical_camera_info = nullptr, 38// .reserved = {nullptr, nullptr} 39//};
可以看到对应的camera_module_t,而里面出现了一个HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM,正好对应宏定义的HMI
这个结构体除了本身熟悉的hw_module_t之后,剩下的就是camera本身的客制化的函数指针
1//hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h
2#define HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR "HMI"
3#define HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM HMI
4
5// hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera_common.h
6typedef struct camera_module {
7 hw_module_t common;
8 int (*get_number_of_cameras)(void);
9 int (*get_camera_info)(int camera_id, struct camera_info *info);
10 int (*set_callbacks)(const camera_module_callbacks_t *callbacks);
11 void (*get_vendor_tag_ops)(vendor_tag_ops_t* ops);
12 int (*open_legacy)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
13 uint32_t halVersion, struct hw_device_t** device);
14 int (*set_torch_mode)(const char* camera_id, bool enabled);
15 int (*init)();
16 int (*get_physical_camera_info)(int physical_camera_id,
17 camera_metadata_t **static_metadata);
18 int (*is_stream_combination_supported)(int camera_id,
19 const camera_stream_combination_t *streams);
20 void (*notify_device_state_change)(uint64_t deviceState);
21 void* reserved[2];
22} camera_module_t;
也就是so打开会找对应的HMI,即HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM所在的实例化结构体。
4.10v4l2_module_methods
这里没有厂商现成的代码,只能先看google原生的代码,即camera.default.so
1//hardware/libhardware/modules/camera/3_4/v4l2_camera_hal.cpp
2static int open_dev(const hw_module_t* module,
3 const char* name,
4 hw_device_t** device) {
5 return gCameraHAL.openDevice(module, name, device);
6}
7
8} // namespace v4l2_camera_hal
9
10static hw_module_methods_t v4l2_module_methods = {
11 .open = v4l2_camera_hal::open_dev};
然后通过传入的id号,打开对应的设备,这里的设备通常是/dev/video0~/dev/video10之间的有效设备
1//hardware/libhardware/modules/camera/3_4/v4l2_camera_hal.cpp
2int V4L2CameraHAL::openDevice(const hw_module_t* module,
3 const char* name,
4 hw_device_t** device) {
5 HAL_LOG_ENTER();
6
7 if (module != &HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM.common) {
8 HAL_LOGE(
9 "Invalid module %p expected %p", module, &HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM.common);
10 return -EINVAL;
11 }
12
13 int id;
14 if (!android::base::ParseInt(name, &id, 0, getNumberOfCameras() - 1)) {
15 return -EINVAL;
16 }
17 // TODO(b/29185945): Hotplugging: return -EINVAL if unplugged.
18 return mCameras[id]->openDevice(module, device);
19}
这里逻辑比较简单,主要是比对传入的module和当前so里面的对比,然后就会加载对应的camera设备
补充一下V4L2CameraHAL的构造,这个构造会更早,打卡camera.default.so的时候会去加载全局变量,这个时候就会被构造
1//hardware/libhardware/modules/camera/3_4/v4l2_camera_hal.cpp 2//这个是静态全局变量 3static V4L2CameraHAL gCameraHAL; 4V4L2CameraHAL::V4L2CameraHAL() : mCameras(), mCallbacks(NULL) { 5 HAL_LOG_ENTER(); 6 // Adds all available V4L2 devices. 7 // List /dev nodes. 8 DIR* dir = opendir("/dev"); 9 if (dir == NULL) { 10 HAL_LOGE("Failed to open /dev"); 11 return; 12 } 13 // 构造函数的时候就会寻找可用的/dev/video*的设备 14 dirent* ent; 15 std::vector<std::string> nodes; 16 while ((ent = readdir(dir))) { 17 std::string desired = "video"; 18 size_t len = desired.size(); 19 if (strncmp(desired.c_str(), ent->d_name, len) == 0) { 20 if (strlen(ent->d_name) > len && isdigit(ent->d_name[len])) { 21 // ent is a numbered video node. 22 nodes.push_back(std::string("/dev/") + ent->d_name); 23 HAL_LOGV("Found video node %s.", nodes.back().c_str()); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 // 测试对V4L2的支持和惟一性. 28 std::unordered_set<std::string> buses; 29 std::string bus; 30 v4l2_capability cap; 31 int fd; 32 int id = 0; 33 for (const auto& node : nodes) { 34 // 这里会打开一次设备 35 fd = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(open(node.c_str(), O_RDWR)); 36 if (fd < 0) { 37 HAL_LOGE("failed to open %s (%s).", node.c_str(), strerror(errno)); 38 continue; 39 } 40 // Read V4L2 capabilities. 41 if (TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(ioctl(fd, VIDIOC_QUERYCAP, &cap)) != 0) { 42 HAL_LOGE( 43 "VIDIOC_QUERYCAP on %s fail: %s.", node.c_str(), strerror(errno)); 44 } else if (!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_VIDEO_CAPTURE)) { 45 HAL_LOGE("%s is not a V4L2 video capture device.", node.c_str()); 46 } else { 47 // If the node is unique, add a camera for it. 48 bus = reinterpret_cast<char*>(cap.bus_info); 49 if (buses.insert(bus).second) { 50 HAL_LOGV("Found unique bus at %s.", node.c_str()); 51 std::unique_ptr<V4L2Camera> cam(V4L2Camera::NewV4L2Camera(id++, node)); 52 if (cam) { 53 mCameras.push_back(std::move(cam)); 54 } else { 55 HAL_LOGE("Failed to initialize camera at %s.", node.c_str()); 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 close(fd); 60 } 61}
- 遍历/dev/videoX节点
- 尝试open节点并查询video能力
- 构建V4L2Camera对象,放入mCameras
源码下载
本文对应的源码,
libhardware可以点击这里
interfaces_camera可以点击这里
参考
[1] 无限无羡. Android 13 Camera HAL启动流程(1), 2023.
[2] 无限无羡. Android 13 Camera HAL启动流程(2), 2023.
[3] 千里马. Android 经典hal开发实战-千里马android framework车载车机手机系统开发, 2023.