C++ operator重载
1200 Words|Read in about 6 Min|本文总阅读量次
源码中出现很多关于operator重载的操作符,但是本文着重讲述关于小括号,指针操作,自定义类型和类型转换。
1介绍
我们在设计一个类的时候,不可避免的需要在某些时候对这个类的实例进行操作符运算,例如比较、自增、自减等。此时就必须在类中重载相应的操作符,如果能够自定义一些规则,就可以让类之间像基本整数一样能够自由的运算。比如string类,可以使用加号+和==等。
1#include <string>
2#include <iostream>
3
4using namespace std;
5
6int main()
7{
8 //使用 + 操作符拼接两个字符串
9 string str1("2023 ");
10 string str2("yangyang48");
11 string str3 = str1 + str2;//"2023 yangyang48"
12 cout << str3 << endl;
13 //使用==来比较两个字符串的内容
14 if (str1 == str2)
15 cout << "str1 = str2" << endl;
16 else if (str1 < str2)
17 cout << "str1 < str2" << endl;
18 else
19 cout << "str1 > str2" << endl;
20
21 return 0;
22}
输出结果
12023 yangyang48
2str1 < str2
多数的C++操作符都可以被重载,重载的操作符(有些情况例外)不必是成员函数,但必须至少有一个操作数是用户定义的类型。下面详细介绍C++对用户定义的操作符重载的限制
-
运算符的优先级(precedence)不可改变。例如,除法的运算优先级永远高于加法。
-
不能引入新的操作符。例如,不能定义operator**()函数来表示求幂。
-
不能重载以下操作符
sizeof——sizeof操作符.——成员操作符.*——成员指针操作符::——作用域解析操作符?:——条件操作符typeid——一个RTTI操作符const_cast——强制类型转换操作符dynamic_cast——强制类型转换操作符reinterpret_cast——强制类型转换操作符static_cast——强制类型转换操作符可以重载的运算符表
=()[]->+-*/%^&` ~=!<>+=-=*=/=%=^=&=` <<>>>>=<<===!=<=>=&&` ` ,->*newdeletenew[]delete[]
2具体demo
2.1仿函数
仿函数(functor),就是使一个类的使用看上去像一个函数。其实现就是类中实现一个operator(),这个类就有了类似函数的行为,就是一个仿函数类了。仿函数是比较特殊的重载符号,为括号()
1#include <string>
2#include <vector>
3#include <iostream>
4
5using namespace std;
6//筛选大于5的数
7class GreaterFive
8{
9public:
10 GreaterFive()
11 {
12 cout << "GreaterFive constructor" << endl;
13 }
14
15 bool operator()(int val)
16 {
17 cout << "GreaterFive functor" << endl;
18 return val > 5;
19 }
20};
21
22class MyCompare{
23public:
24 //排序从大到小
25 bool operator()(int v1,int v2)
26 {
27 return v1 > v2;
28 }
29};
30int main()
31{
32 vector v{2,0,2,3,0,7,0,8};
33 //传入的GreaterFive()是一个匿名的对象,通过传入的匿名对象调用这个对象的仿函数
34 vector<int>::iterator iter = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());
35 for(int i = 0;i <v.size(); i++)
36 {
37 cout << v[i] << "\t";
38 }
39 cout << endl;
40 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare());
41 for(int i = 0;i <v.size(); i++)
42 {
43 cout << v[i] << "\t";
44 }
45}
这里可以看到处理STL中的查找函数和排序函数,都使用到了仿函数。
这里的仿函数作用原理也是比较巧妙,利用匿名的构造函数调用传入对象,然后STL内部会调用对应的仿函数达到目的。
另外特别的是,如果仿函数的返回类型为bool类型,那么可以称为谓词,有几个参数可以称为几元谓词。
1//一元谓词
2bool GreaterFive::operator()(int val);
3//二元谓词
4bool MyCompare::operator()(int v1,int v2);
2.2指针/引用相关运算符重载
在强指针中,出现了使用指针运算重载的运算符操作,具体可以查看Android智能指针解析
1//system_core/blob/HEAD/libutils/include/utils/StrongPointer.h
2template<typename T>
3class sp {
4public:
5 ...
6 // Accessors
7 inline T& operator* () const { return *m_ptr; }
8 inline T* operator-> () const { return m_ptr; }
9 inline T* get() const { return m_ptr; }
10 inline explicit operator bool () const { return m_ptr != nullptr; }
11};
如果这个时候调用
1using namespace android;
2class A : public RefBase
3{
4public:
5 virtual ~A(){};
6 int value()
7 {
8 return 723;
9 }
10};
11
12int main()
13{
14 sp<A> a = new A();
15 cout << a->value() << endl;
16 return 0;
17}
输出结果
1723
上面的a->value,这里的a并不是一个指针(a保存的不是一个地址,a是一个sp<a>的临时变量),但是有一个运算符重载,这个运算符重载相当于是指针的运算。
1a->value();
2//等价于 a.operator->()->value();
3//等价于 m_ptr->value();
4//等价于 (*m_ptr).value();这里才真正调用到了默认的指针运算方式,调用到函数value
2.3自定义字符串重载
这里举一个源码中的操作,用于FPS的计算,即1/60s的计算
1//frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Scheduler/include/scheduler/Fps.h
2class Fps {
3public:
4 constexpr Fps() = default;
5
6 static constexpr Fps fromValue(float frequency) {
7 return frequency > 0.f ? Fps(frequency, static_cast<nsecs_t>(1e9f / frequency)) : Fps();
8 }
9
10 static constexpr Fps fromPeriodNsecs(nsecs_t period) {
11 return period > 0 ? Fps(1e9f / period, period) : Fps();
12 }
13
14 constexpr bool isValid() const { return mFrequency > 0.f; }
15
16 constexpr float getValue() const { return mFrequency; }
17 int getIntValue() const { return static_cast<int>(std::round(mFrequency)); }
18
19 constexpr nsecs_t getPeriodNsecs() const { return mPeriod; }
20
21private:
22 constexpr Fps(float frequency, nsecs_t period) : mFrequency(frequency), mPeriod(period) {}
23
24 float mFrequency = 0.f;
25 nsecs_t mPeriod = 0;
26};
27
28struct FpsRange {
29 Fps min = Fps::fromValue(0.f);
30 Fps max = Fps::fromValue(std::numeric_limits<float>::max());
31
32 bool includes(Fps) const;
33};
34//类外定义
35constexpr Fps operator""_Hz(unsigned long long frequency) {
36 return Fps::fromValue(static_cast<float>(frequency));
37}
38//类外定义
39constexpr Fps operator""_Hz(long double frequency) {
40 return Fps::fromValue(static_cast<float>(frequency));
41}
这个类,只有两个内部私有变量,一个是外部传入定义的帧率,可以是60.0,也可以是其他浮点数,后一个参数即为转换为毫秒的数,对应具体的1/mFrequency的值。这个封装起来非常巧妙,使用默认的例子即可。
1//使用方式
2// Frames per second, stored as floating-point frequency. Provides conversion from/to period in
3// nanoseconds, and relational operators with precision threshold.
4//
5// const Fps fps = 60_Hz;
6//
7// using namespace fps_approx_ops;
8// assert(fps == Fps::fromPeriodNsecs(16'666'667));
9//
完整版
1#include <iostream>
2#include <stdio.h>
3using namespace std;
4class Fps {
5public:
6 constexpr Fps() = default;
7
8 static constexpr Fps fromValue(float frequency) {
9 return frequency > 0.f ? Fps(frequency, static_cast<long long>(1e9f / frequency)) : Fps();
10 }
11
12 static constexpr Fps fromPeriodNsecs(long long period) {
13 return period > 0 ? Fps(1e9f / period, period) : Fps();
14 }
15
16 constexpr bool isValid() const { return mFrequency > 0.f; }
17
18 constexpr float getValue() const { return mFrequency; }
19
20 constexpr long long getPeriodNsecs() const { return mPeriod; }
21
22private:
23 constexpr Fps(float frequency, long long period) : mFrequency(frequency), mPeriod(period) {}
24
25 float mFrequency = 0.f;
26 long long mPeriod = 0;
27};
28
29struct FpsRange {
30 Fps min = Fps::fromValue(0.f);
31
32 bool includes(Fps) const;
33};
34//类外定义
35constexpr Fps operator""_Hz(unsigned long long frequency) {
36 printf("unsigned long long frequency %llu\n", frequency);
37 return Fps::fromValue(static_cast<float>(frequency));
38}
39//类外定义
40constexpr Fps operator""_Hz(long double frequency) {
41 printf("unsigned long double frequency %llf\n", frequency);
42 return Fps::fromValue(static_cast<float>(frequency));
43}
44
45int main()
46{
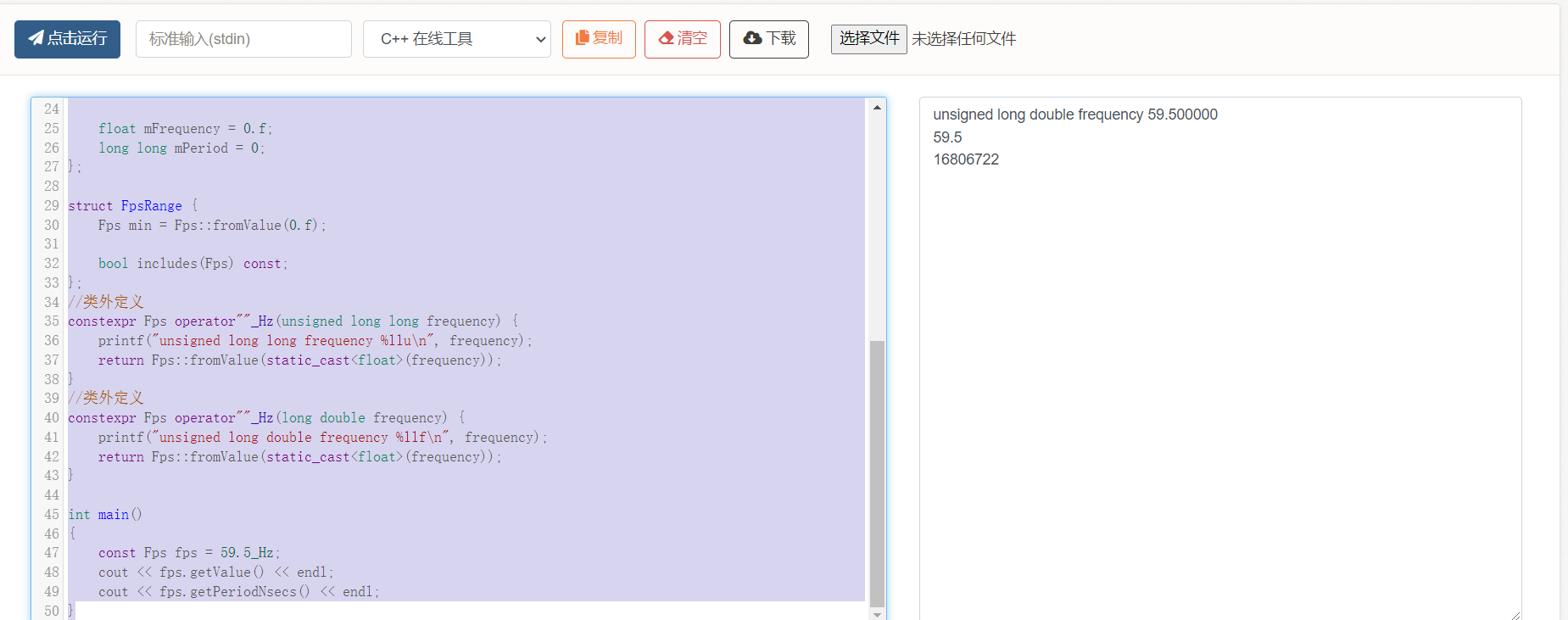
47 const Fps fps = 59.5_Hz;
48 cout << fps.getValue() << endl;
49 cout << fps.getPeriodNsecs() << endl;
50}
输出结果
1//60
2//16666667
359.5
416806722
另外上面加printf或者cout日志,在C++20会出错,但是低版本使用printf不会报错。constexpr函数中原因是使用了non-‘constexpr’的函数,具体可以点击这里。
2.4类型转换
这里类型转换,实际上就将类强制转化成某成类型(多见基本类型)
1#include <iostream>
2using namespace std;
3class A{
4public:
5 A(int num) : mNum(num) {
6 cout << "A constructor " << this << endl;
7 }
8 ~A(){
9 cout << "A destructor " << this << endl;
10 }
11 //使用显示方式,使用explicit关键字后不支持隐式转换
12 explicit operator int() const
13 {
14 cout << "A operator int " << this << endl;
15 return mNum;
16 }
17private:
18 int mNum = 0;
19};
20int main()
21{
22 A a(2023);
23 //类本身转换成int类型和0723就行运算
24 cout << (int)a + 0723 << endl;
25 //cout << static_cast<int>(a) + 0723 << endl;
26}
输出结果为
1A constructor 0x72c59ffa2c
2A operator int 0x72c59ffa2c
32490
4A destructor 0x72c59ffa2c
进一步的,转换成其他类型
1#include <iostream>
2using namespace std;
3class B{
4public:
5 B(){
6 cout << "B constructor " << this << endl;
7 }
8
9 ~B(){
10 cout << "B destructor " << this << endl;
11 }
12 void print()
13 {
14 cout << "B print " << this << endl;
15 }
16};
17
18class A{
19public:
20 A(int num, B& b) : mNum(num), mB(b) {
21 cout << "A constructor " << this << endl;
22 }
23 ~A(){
24 cout << "A destructor " << this << endl;
25 }
26 //默认隐式转换
27 explicit operator B() const
28 {
29 cout << "A operator int " << this << endl;
30 return mB;
31 }
32private:
33 int mNum = 0;
34 B mB;
35};
36
37int main()
38{
39 B b;
40 A a(2023, b);
41 static_cast<B>(a).print();
42}
输出结果
1B constructor 0xb33cbffc5e
2A constructor 0xb33cbffc54
3A operator int 0xb33cbffc54
4B print 0xb33cbffc5f
5B destructor 0xb33cbffc5f
6A destructor 0xb33cbffc54
7B destructor 0xb33cbffc58
8B destructor 0xb33cbffc5e
转换结果虽好,但不建议不同类型之间转换,一般这种类转换成其他类型并不是很多见,最多会用到在大括号的隐式类型转化中,具体可以点击这里查看。
3总结
总的来说,操作符的高阶玩法,远远不止上述,上述也只是笔者遇到的一个小总结。如果后续还出现一些比较高阶的用法会持续更新。另外操作符的重载虽然可以重载new和delete,但是不建议去修改,因为这样使用很容易造成逻辑混乱,导致出现意想不到的异常。
关于上述的在线编译
点击这里。使用的是菜鸟教程的c++编译器,运行速度还不较快,也不容易挂掉
参考
[1] 时空-大海水, std::chrono::duration详解, 2017.
[2] Iron Fist, C++ error: Call to non-constexpr function, 2020.
[3] 时空-大海水, std::chrono::duration详解, 2017.
[4] shadow_xwl, C++操作符重载, 2022.