Java Thread
1000 Words|Read in about 5 Min|本文总阅读量次
除了本身的并发编程,再聊聊Thread本身的特性。
0简介
之前的并发编程中多少提到了Java的Thread,但是关于Thread还想再聊聊自己的看法。
除了主流对Thread的用法,还有关于Thread.sleep(0)的方法使用
另外,Java端要获取Linux层的线程id的话,应该通过什么方式呢
1Thread.Sleep(0)
下面这段代码注释写着保护GC。这个代码是想要“触发”GC,而不是“避免”GC,或者说是“避免”时间很长的 GC。从这个角度来说,程序里面的注释其实是在撒谎或者没写完整。
1//这段源码来自于RocketMQ 的源码
2for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < this.fileSize; i += MappedFile.OS_PAGE_SIZE, j++) {
3 byteBuffer.put(i, (byte) 0);
4 // force flush when flush disk type is sync
5 if (type == FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH) {
6 if ((i / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE) >= pages) {
7 flush = i;
8 mappedByteBuffer.force();
9 }
10 }
11
12 // prevent gc
13 if (j % 1000 == 0) {
14 log.info("j={}, costTime={}", j, System.currentTimeMillis() - time);
15 time = System.currentTimeMillis();
16 try {
17 Thread.sleep(0);
18 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
19 log.error("Interrupted", e);
20 }
21 }
22 }
原理
Thread.sleep(0)就是“触发操作系统立刻重新进行一次CPU竞争”。结果也许是当前线程仍然获得CPU控制权,也许会换成别的线程获得CPU控制权。
这样看来,这个场面就有意思了——可能有些人是PPMM,因此具有高优先级,于是她就可以经常来吃蛋糕。可能另外一个人是个丑男,而去很ws,所以优先级特别低,于是好半天了才轮到他一次(因为随着时间的推移,他会越来越饥饿,因此算出来的总优先级就会越来越高,因此总有一天会轮到他的)。而且,如果一不小心让一个大胖子得到了刀叉,因为他饭量大,可能他会霸占着蛋糕连续吃很久很久,导致旁边的人在那里咽口水。。。
而且,还可能会有这种情况出现:操作系统现在计算出来的结果,5号PPMM总优先级最高,而且高出别人一大截。因此就叫5号来吃蛋糕。5号吃了一小会儿,觉得没那么饿了,于是说“我不吃了”(挂起)。因此操作系统就会重新计算所有人的优先级。因为5号刚刚吃过,因此她的饥饿程度变小了,于是总优先级变小了;而其他人因为多等了一会儿,饥饿程度都变大了,所以总优先级也变大了。不过这时候仍然有可能5号的优先级比别的都高,只不过现在只比其他的高一点点——但她仍然是总优先级最高的啊。因此操作系统就会说:5号mm上来吃蛋糕……(5号mm心里郁闷,这不刚吃过嘛……人家要减肥……谁叫你长那么漂亮,获得了那么高的优先级)。
那么,Thread.Sleep 函数是干吗的呢?还用刚才的分蛋糕的场景来描述。上面的场景里面,5号MM在吃了一次蛋糕之后,觉得已经有8分饱了,她觉得在未来的半个小时之内都不想再来吃蛋糕了,那么她就会跟操作系统说:在未来的半个小时之内不要再叫我上来吃蛋糕了。这样,操作系统在随后的半个小时里面重新计算所有人总优先级的时候,就会忽略5号mm。Sleep函数就是干这事的,他告诉操作系统“在未来的多少毫秒内我不参与CPU竞争”。
Thread.sleep(0)相当于插入了一个安全点。这样就可以避免你的程序
GC线程长时间等待。也就是所谓的GC削峰。
Java虚拟机在进行GC的时候,有着STW的特性。即Stop The World,停顿所有Java执行进程。既然有
STW的机制,那么GC是随时发起的吗?并是不,Java虚拟机利用了一个安全点机制Safepoint,只有程序到达安全点的时候才能够进行GC。有了安全点的设定,也就决定了用户程序执行时并非在代码指令流的任意位置都能够停顿下来开始垃圾收集,而是强制要求必须执行到达安全点后才能够暂停。可数循环:如果循环次数比较少的话,执行时间应该不会太长,**使用
int类型或者范围更小的数据类型作为索引值,这种是不会被放置安全点的。**循环如果没有结束。程序就无法走到安全点,就无法GC。不可数循环:反之,如果使用
long这样范围更大的类型作为索引的循环,就叫做不可数循环。此时循环过程中就会插入安全点。单次循环体结束的时候,就可以进入安全点,无需等待整个循环跑完。一个线程在运行
native方法后,返回到Java线程后,必须进行一次safepoint的检测。Thread.sleep(0)正好为native方法,需要做一个安全点检测。在这里的循环中,相当于放置一个 Safepoint 呢,以达到避免 GC 线程长时间等待,相当于让可数循环变成不可数循环那样,无需等待整个循环跑完。1//通常num需要两个子线程结束才能给出结果 2public class MainTest { 3 4 public static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0); 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 7 Runnable runnable=()->{ 8 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) { 9 num.getAndAdd(1); 10 } 11 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束!"); 12 }; 13 14 Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable); 15 Thread t2 = new Thread(runnable); 16 t1.start(); 17 t2.start(); 18 Thread.sleep(1000); 19 System.out.println("num = " + num); 20 } 21}1)但是把int修改成long变成不可数循环即可
1//通常num需要两个子线程结束才能给出结果 2public class MainTest { 3 4 public static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0); 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 7 Runnable runnable=()->{ 8 //这里把int修改成long,变成不可数循环,进入安全点无需等待循环结束 9 for (long i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) { 10 num.getAndAdd(1); 11 } 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束!"); 13 }; 14 15 Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable); 16 Thread t2 = new Thread(runnable); 17 t1.start(); 18 t2.start(); 19 Thread.sleep(1000); 20 System.out.println("num = " + num); 21 } 22}2)或者是把引入Thread.sleep(0),可以达到同样效果,无需等待循环结束
1//引入Thread.sleep(0) 2public class MainTest { 3 4 public static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0); 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 7 Runnable runnable=()->{ 8 for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) { 9 num.getAndAdd(1); 10 // prevent gc 11 if (i % 1000 == 0) { 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(0); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"执行结束!"); 20 }; 21 22 Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable); 23 Thread t2 = new Thread(runnable); 24 t1.start(); 25 t2.start(); 26 Thread.sleep(1000); 27 System.out.println("num = " + num); 28 } 29}
2获取Tid
2.1从源码中找线索
1public class Thread implements Runnable {
2
3 private volatile long nativePeer;
4 private volatile String name;
5 private int priority;
6 /* For autonumbering anonymous threads. */
7 private static int threadInitNumber;
8 private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() {
9 return threadInitNumber++;
10 }
11
12 private long tid;
13 private static long threadSeqNumber;
14 //thread构造方法
15 public Thread() {
16 init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
17 }
18
19 public Thread(Runnable target) {
20 init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
21 }
22
23 public Thread(String name) {
24 init(null, null, name, 0);
25 }
26 //初始化Thread
27 private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
28 long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) {
29 if (name == null) {
30 throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
31 }
32
33 this.name = name;
34 init2(parent);
35 this.stackSize = stackSize;
36
37 //这里面的tid不是真实linux的tid,这个是按次序在java层分配的id
38 tid = nextThreadID();
39 }
40
41}
2.1.1startThread
1//startThread创建线程工作
2public synchronized void start() {
3 //如果线程已启动过,抛出异常
4 if (started)
5 throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
6 //添加线程到 group中
7 group.add(this);
8
9 started = false;
10 try {
11 //调用native 函数进行真正的线程创建工作,传入2个参数,分别为线程函数栈大小及daemon书写
12 nativeCreate(this, stackSize, daemon);
13 started = true;
14 } finally {
15 try {
16 //创建流程失败的逻辑处理
17 if (!started) {
18 group.threadStartFailed(this);
19 }
20 } catch (Throwable ignore) {
21 /* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
22 it will be passed up the call stack */
23 }
24 }
25}
2.1.2Thread_nativeCreate
调用到真实的thread线程创建工作
1//art/runtime/thread.cc
2void Thread::CreateNativeThread(JNIEnv* env, jobject java_peer, size_t stack_size, bool is_daemon) {
3 ...
4}
这里面涉及到的代码比较复杂,会按照功能划分三段new Thread、pthread_create、Thread::Init
1//art/runtime/thread.h
2//tid保存的地方tls32_结构体中
3struct PACKED(4) tls_32bit_sized_values {
4 typedef uint32_t bool32_t;
5 union StateAndFlags state_and_flags;
6 int suspend_count GUARDED_BY(Locks::thread_suspend_count_lock_);
7 int debug_suspend_count GUARDED_BY(Locks::thread_suspend_count_lock_);
8 uint32_t thin_lock_thread_id;
9 // System thread id.
10 uint32_t tid;
11 ...
12} tls32_;
我们现在知道 tid是保存在 tls32_结构体 中,并且其位于 Thread对象的开头,以Android11源码来看, tid 处于第16个字节(位于 state_and_flags、suspend_count、debug_suspend_count、think_lock_thread_id之后)开头。 因此我们只要能够获取 native层 该thread对象的指针 就可以通过 内存偏移的方式 获取tid。
2.2获取 Java Thread对象对应的tid
1package com.example.nativetid;
2
3import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
4
5import android.os.Bundle;
6import android.util.Log;
7import android.widget.TextView;
8
9import com.example.nativetid.databinding.ActivityMainBinding;
10
11import java.lang.reflect.Field;
12
13public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
14
15 // Used to load the 'native-lib' library on application startup.
16 static {
17 System.loadLibrary("native-lib");
18 }
19
20 private ActivityMainBinding binding;
21 private final String TAG = "MainActivity";
22
23 @Override
24 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
25 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
26
27 binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
28 setContentView(binding.getRoot());
29
30 // Example of a call to a native method
31 TextView tv = binding.sampleText;
32 tv.setText(stringFromJNI());
33 try {
34 init();
35 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
36 e.printStackTrace();
37 }
38 }
39
40 private void init() throws IllegalAccessException {
41 Thread thread = new Thread("demo_thread"){
42 @Override
43 public void run() {
44 try {
45 sleep(10 * 1000);
46 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
47 e.printStackTrace();
48 }
49 Log.d(TAG, "->>>Thread对象的run方法被执行了");
50 }
51 };
52 //线程启动
53 thread.start();
54 long peer = getNativePeer(thread);
55 Log.d(TAG, "->>>tid = " + getTid(peer));
56
57 }
58
59 public static final long getNativePeer(Thread t)throws IllegalAccessException{
60 try {
61 Field nativePeerField = Thread.class.getDeclaredField("nativePeer");
62 nativePeerField.setAccessible(true);
63 Long nativePeer = (Long) nativePeerField.get(t);
64 return nativePeer;
65 } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
66 throw new IllegalAccessException("failed to get nativePeer value");
67 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
68 throw e;
69 }
70 }
71 /**
72 * A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library,
73 * which is packaged with this application.
74 */
75 public native String stringFromJNI();
76 public static native int getTid(long nativePeer);
77}
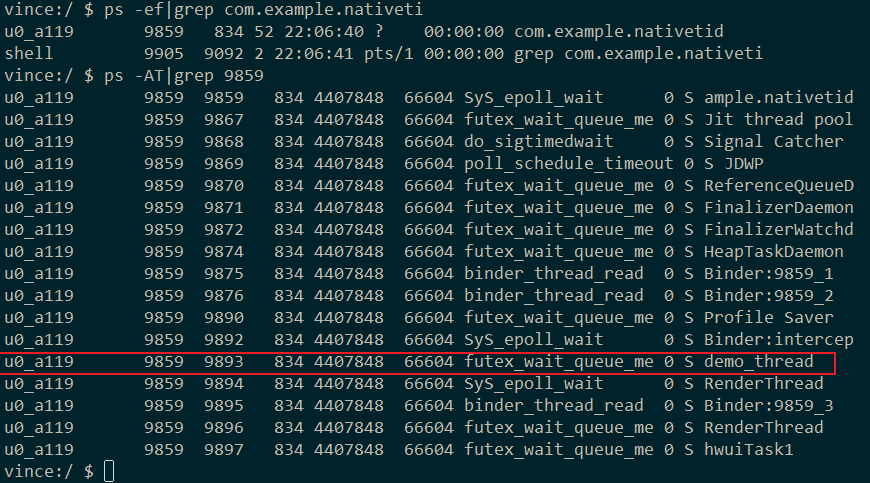
笔者以红米手机测试ok
本文源码
下载点击这里